In today’s digital age, cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate. At the core of cloud computing lie three distinct service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
With its numerous benefits, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, the cloud has become an essential tool for driving business growth.
This article is a comprehensive guide that dives deep into these cloud service models, providing insights and knowledge to harness their potential and propel businesses forward.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Cloud Service Models.
- Driving Business Growth with Cloud Computing
- Conclusion
Understanding IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
The three cloud service models, namely IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, have their unique characteristics and use cases.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
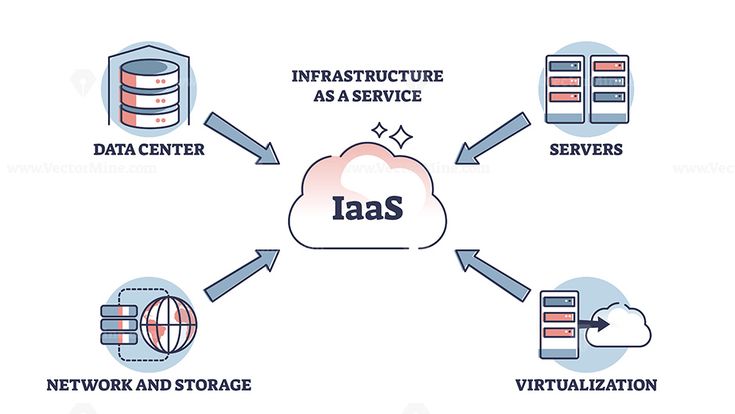
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offers businesses virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, delivered over the Internet. This model allows organizations to offload the costs and complexities of managing physical infrastructure while providing the flexibility to scale resources on demand.
Organizations do not have to buy physical infrastructure to set up networks with multiple connections like hub, switches, routers, or storage devices like multiple hard drives. Organizations can use these computing resources through cloud service providers.
Applications of IaaS in Businesses
Data Storage and Backup
IaaS providers offer scalable and secure storage solutions, allowing businesses to store, manage, and use vast amounts of data without worrying about physical infrastructure.
Development and Testing Environments
IaaS platforms provide a flexible environment for developers to create, test, and deploy applications.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI):
IaaS supports Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), allowing businesses to provide employees with virtual desktops that can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This has led to the wide use of virtual machines (VMs).
With virtual machines, employees can have access to a virtualized “PC” with just their credentials to sign in. This way, an employee can have access to a Windows PC on the cloud, even if they travel to another country without carrying a physical laptop. Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) are instances of IaaS Applications
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
IaaS plays a crucial role in disaster recovery planning. Businesses can replicate their critical infrastructure in the cloud, ensuring continuity in the face of unexpected events. For example, bank infrastructure services that ensure USSD, mobile apps run for customers can be replicated in the cloud. This is to ensure services keep running if there’s downtime.
Advantages of IaaS in Businesses
- Security
- Saves Cost
- Scalability and Flexibility
Disadvantages of IaaS in Businesses
- The businesses are in charge of configuring and managing the services.
- Data Security Concerns.
- Reliance on Cloud provider.
Get an in-depth knowledge of different Cloud services with our Cloud Computing Courses!
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
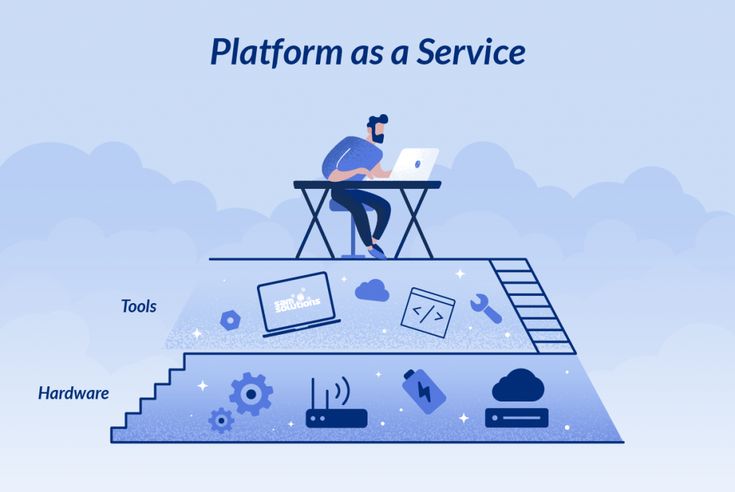
Platform as a Service (PaaS) goes a step further by providing a development platform that simplifies the process of building, testing, and deploying applications. By leveraging PaaS, businesses can focus on their software development efforts without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
Applications of Paas in Businesses
Accelerated Application Development
PaaS provides a set of development tools, frameworks, and services that streamline the application development process. PaaS applications for development are Visual Studio Code (VSCode) and Azure Web Apps.
Database Management:
PaaS platforms often include managed database services. This simplifies database administration tasks such as backups, updates, and scaling, allowing developers to concentrate on application logic rather than database maintenance. A PaaS application for Database management (DBMS) is Azure SQL Database.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
PaaS platforms often integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, automating the processes of code integration, testing, and deployment. A PaaS application useful for CI/CD is GitHub.
Advantages of Paas in Businesses
- PaaS supports multiple programming languages.
- PaaS simplifies the development process.
- PaaS tools are typically used to focus on innovation.
Disadvantages of Paas in Businesses
- Data Security Concerns
- Challenges with integration
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)

Software as a Service (SaaS) offers ready-to-use software applications delivered over the Internet. This model eliminates the need for organizations to develop and maintain their software, empowering them to access a wide range of applications for various business functions, such as customer relationship management (CRM), human resources (HR), and enterprise resource planning (ERP).
Applications of Saas in Businesses
Collaboration and Communication Tools
SaaS provides a variety of collaboration and communication tools, including email services, messaging platforms, and project management applications. Some SAAS tools are Microsoft Word, Microsoft Outlook, and Google Docs.
These tools facilitate seamless communication and collaboration among team members, whether they are in the same office or working remotely.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
SaaS-based CRM solutions are widely adopted by businesses to manage customer interactions, sales, and marketing efforts. These applications help organizations streamline customer-related processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve sales efficiency.
Banks and insurance firms create, build and use Saas CRM tools for their customers. HubSpot CRM, Zoho, Zendesk, and Slack are CRM software.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
SaaS-based ERP solutions integrate various business processes such as finance, human resources, and supply chain management. These platforms provide a centralized system for managing critical business functions, promoting efficiency, and ensuring data consistency. Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP
Human Resources Management (HRM)
SaaS HRM applications offer features for employee onboarding, payroll processing, performance management, and workforce analytics. These tools simplify HR processes, enabling organizations to focus on talent management and employee engagement. Bamboo HR
Accounting and Finance Software
SaaS-based accounting and finance applications assist businesses in managing financial transactions, generating reports, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. These tools provide real-time insights into financial performance and support strategic decision-making. Quickbooks and BusyWin are SaaS accounting software.
E-commerce Platforms
Many e-commerce businesses leverage SaaS platforms for their online storefronts. These platforms offer features such as inventory management, payment processing, and order fulfilment, allowing businesses to establish and manage their online presence effectively. Stripe is an example of a SaaS e-commerce software for payment.
Document Management and Collaboration
SaaS applications for document management and collaboration facilitate secure sharing, editing, and storage of documents. These tools enhance teamwork and ensure that employees have access to the latest version of documents, regardless of their location. An example of document management is SharePoint.
Advantages of Saas in Businesses
- Improved Collaboration and Communication for real-time editing.
- Global Availability
- Subscription Model Predictability.
- Reduced IT Management Burden.
- Accessibility and Remote Work.
Disadvantages of Saas in Businesses
- Data Security and Privacy
- Limited Customization
- Challenges with Integration
- Cost of subscription
Driving Business Growth with Cloud Computing
Saas, Iaas, and Paas applications drive business growth through innovations and solutions to problems. Through these applications, businesses can improve and scale up. The use of these applications have greatly influenced remote work, allowing companies to have employees from different countries and regions.
It is essential for businesses, tech professionals and individuals who want to transition to tech to harness the potential in these applications.
Conclusion
The cloud has become a key enabler of business growth, providing organizations with the agility and flexibility required to thrive in today’s digital landscape. IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS serve as an invaluable resource for individuals and businesses seeking to navigate the world of cloud computing. It is essential to have the knowledge and tools to unlock the full potential of the cloud for business growth. This greatly impacts how individuals and businesses interact with the cloud.