The Exchange Mailbox plays a crucial role in facilitating communication within an organization. It is managed by the Microsoft Exchange server. It serves as a central hub for employees to send, receive, and organize emails.
This article will cover aspects of Microsoft Exchange, the mailboxes and managing permissions of mailboxes in Exchange Online.
Key Aspects of the Exchange Mailbox
Let’s dive into the key aspects of the Exchange Mailbox.
1. Purpose and Function
– The Exchange Mailbox acts as a bridge between employees, enabling seamless communication via email.
– It handles incoming and outgoing messages, calendar invitations, contacts, and other collaborative features.
2. Issuance and Types
– Organizations issue Exchange Mailboxes to their employees, typically as work or school accounts.
– These accounts are associated with the organization’s domain (e.g., [email protected]).
– Users access their mailboxes through email clients (such as Outlook) or web interfaces (like Outlook Web App).
3. Mailbox Management
Administrators are required to manage mailboxes in Exchange. After creating a mailbox, admins continue to manage it throughout its lifecycle.
– Common management tasks include:
– Adding Features: Administrators can enhance mailboxes by enabling additional features like shared calendars, distribution lists, and resource mailboxes (e.g., conference rooms).
– Setting Permissions: Administrators grant access permissions to users. These permissions can be added on the Exchange Admin Center (EAC), Office 365 Admin Center and PowerShell.
– Full Access: Allows a user to access another user’s mailbox.
– Send As/On Behalf Of: Permits sending emails on behalf of someone else. The delegates can still be identified as the senders, not as the mailbox owner.
– Folder-Level Permissions: Controls access to specific mailbox folders.
– Quota Management: Administrators monitor mailbox size and enforce storage limits.
– Archiving and Retention: Implementing retention policies ensures data compliance and efficient storage.
4. Security Considerations
– Exchange Mailboxes contain sensitive information, so security is paramount.
– Measures include:
– Authentication: Users must authenticate to access their mailboxes.
– Encryption: Data transmitted between clients and the Exchange server is encrypted.
– Anti-Spam and Anti-Malware: Built-in filters protect against malicious emails.
– Auditing: Monitoring mailbox activity helps detect anomalies.
Understanding Exchange Mailboxes
There are three mailboxes that permissions can be added to for users. They are User mailboxes, shared mailbox and resource mailbox.
1. User MailBox
This mailbox is tied to individuals. It operates with Active Directory Account that allows the user to send and receive emails; store events calendar, notes, and create meetings and appointments. Each user must however have the Office 365 license to access it.
2. Shared Mailbox
This type of mailbox is used by business organizations as multiple people can access it without buying licenses for each person. It is most suitable as a departmental inbox, however, it falls short in its storage as it only has a storage capacity of 50GB.
3. Resource Mailbox
This mailbox is used to request for resources, rather than send and receive messages. It is used by organizations to schedule meetings based on availability. It does not require any license and is available on the Office 365 free plan. Examples of this type of mailbox include the room mailbox.
Manage Mailbox Permissions Using the Exchange Admin Center
Follow these steps to set permissions in the Exchange Admin Center.
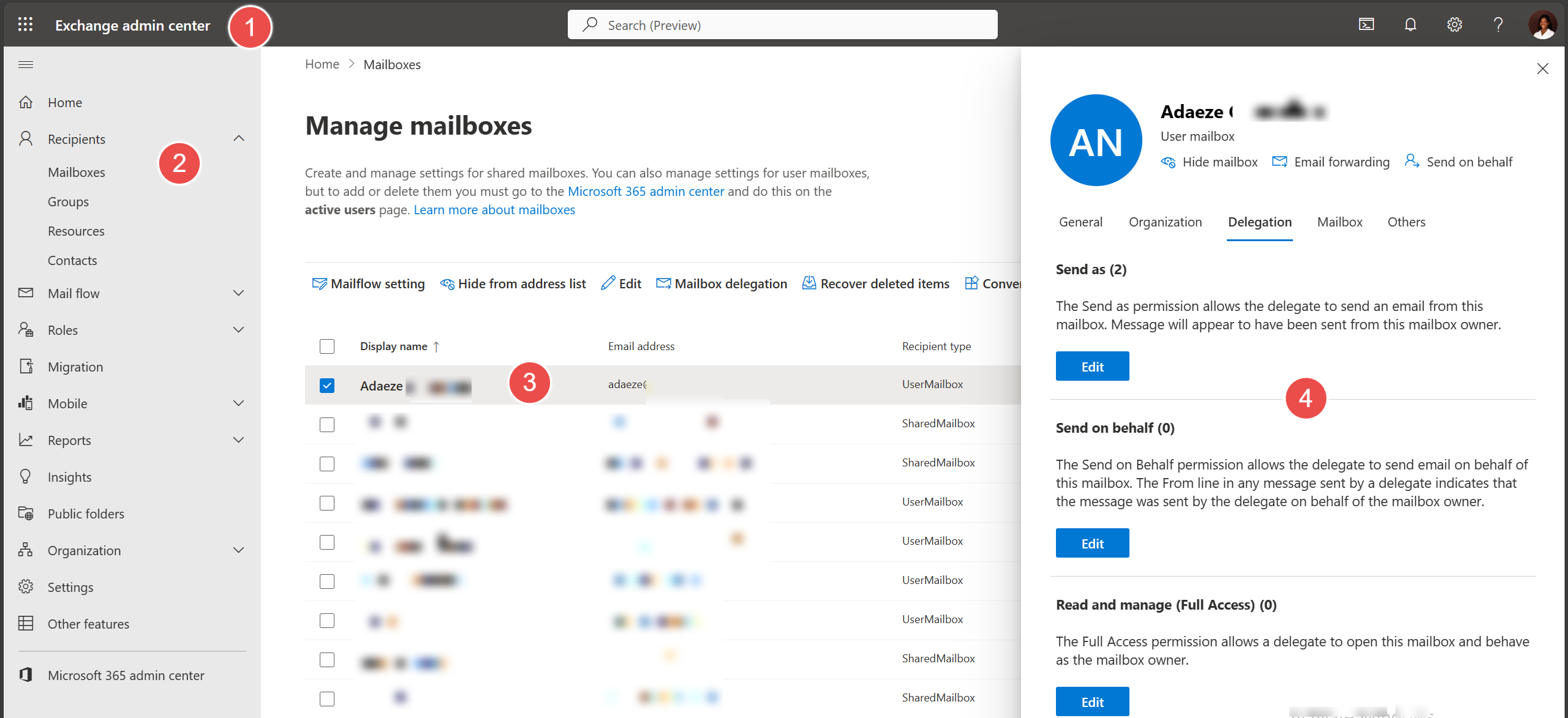
1. Sign in to the Exchange Admin Center with your admin account.
2. Go to Recipients > Mailboxes on the left to update mailbox permissions.
3. Select any mailboxes to update before selecting Mailbox delegation.
4. Enter the delegate’s login or email address and choose your desired permission from the selection.
Setting Mailbox Permissions in M365 Admin Center
The Microsoft 365 Admin Center has several Exchange Admin Center functionalities.
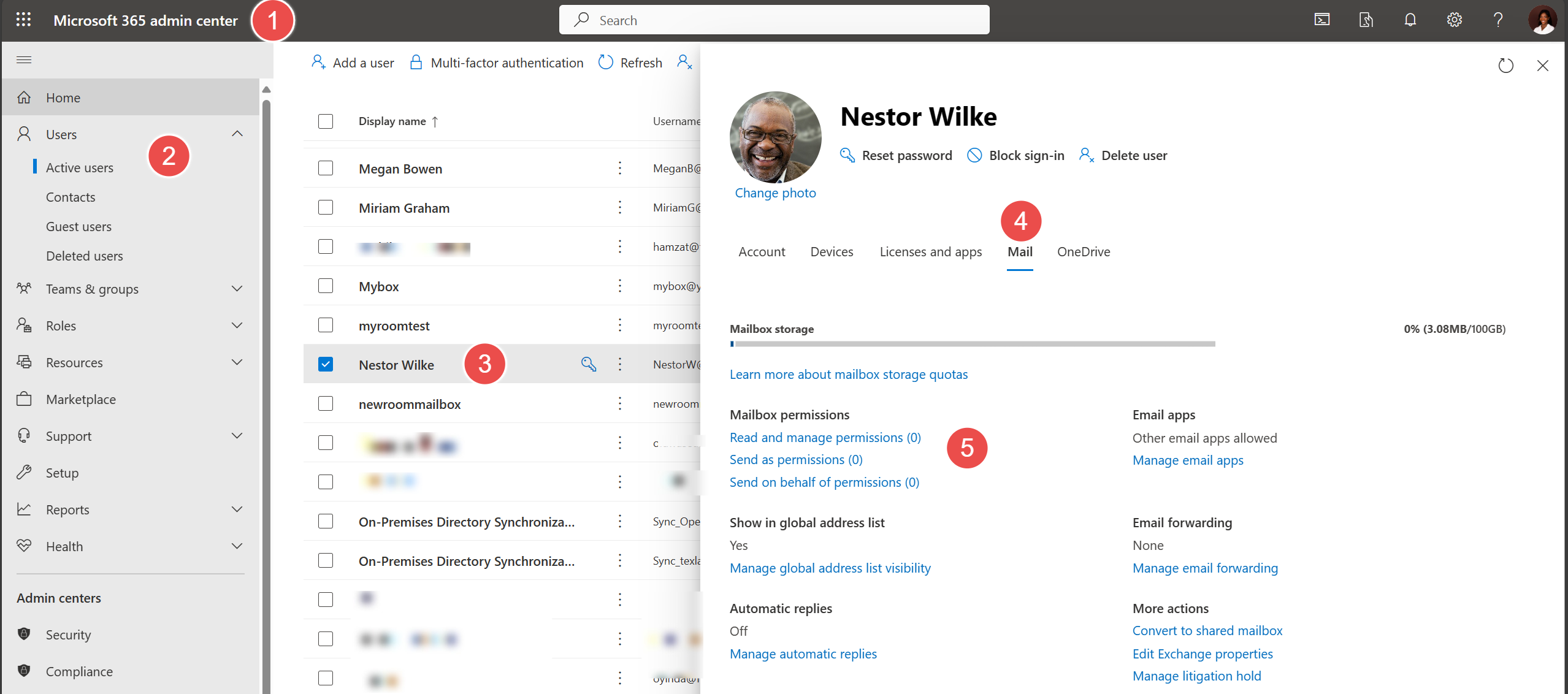
1. Open the Office 365 Admin Center with your admin account.
2. Go to Users – Active users for mailbox settings.
3. Open the account you wish to add permission to.
4. Click Mail on the right
5. Manage mailbox permissions. Add other accounts to the three permission tiers here.
Mailbox Permissions with PowerShell
To add access to another mailbox or a shared mailbox, you can use Exchange Online PowerShell. Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell to do this.
PowerShell command
- Full Access Permission
The Add-MailboxPermission with recipient, delegate, and permission level options adds Full Access permission. InheritanceType controls inheritance settings, and -AutoMapping decides if the mailbox is automatically added to the delegate’s Outlook profile.
[aux_code language=”PowerShell” theme=”tomorrow” title=”” extra_classes=””]Add-MailboxPermission -Identity <MailboxIdentity> -User <DelegateIdentity> -AccessRights FullAccess -InheritanceType All [-AutoMapping $false][/aux_code]
This example assigns the delegate Victoria the Full Access permission to the mailbox of Temitope.
[aux_code language=”PowerShell” theme=”tomorrow” title=”” extra_classes=””]Add-MailboxPermission -Identity [email protected] -User [email protected] -AccessRights FullAccess -InheritanceType All [-AutoMapping $false][/aux_code]
Interested in being a Microsoft 365 Expert? Register for Evolve Connect’s Microsoft 365 BootCamp.
2. Send As Permission
The Add-RecipientPermission cmdlet grants Send As permission. This command calls the delegate the -Trustee, not the user.
[aux_code language=”PowerShell” theme=”tomorrow” title=”” extra_classes=””]Add-RecipientPermission -Identity “[email protected]” -Trustee “[email protected]” – AccessRights SendAs[/aux_code]
This example assigns the delegate Victoria the Send As permission to the mailbox of Temitope.
[aux_code language=”PowerShell” theme=”tomorrow” title=”” extra_classes=””]Add-RecipientPermission -Identity “[email protected]” -Trustee “[email protected]” -AccessRights SendAs[/aux_code]
3. Send On Behalf
Use Set-Mailbox with –GrantSendOnBehalfTo to grant Send on Behalf access to another mailbox.
This example assigns the delegate Victoria the Send on Behalf permission to the mailbox of Temitope.
[aux_code language=”PowerShell” theme=”tomorrow” title=”” extra_classes=””]Set-Mailbox -Identity [email protected] -GrantSendOnBehalfTo [email protected][/aux_code]
For further information, see Microsoft Documentation.
Conclusion
Managing mailbox permissions in Exchange Online is made easy for an administrator through the portal. In summary, the Exchange Mailbox serves as a vital communication lifeline within organizations, enabling efficient collaboration and information exchange among employees.