Cloud computing is one of the most in-demand and lucrative professions in information technology. Organizations are replacing their infrastructure with cloud services and keeping sensitive, critical data in the cloud. Cloud engineering can be used by enterprises in any area, including banking, healthcare, aviation, information technology, and manufacturing. Running businesses using the cloud has encouraged remote work for businesses. This has led businesses and organizations to adopt cloud computing.
In this blog, you will understand the fundamentals of Cloud Computing and how it works.
Table of Content
-What is Cloud Computing?
-Benefits of Cloud computing
-Components of Cloud Computing
-Cloud Deployment Models
-Conclusion
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to delivering IT resources like computing, storage, database, networking, analytics, intelligence, and more over the internet.
In simple words, Cloud computing is a service that lets you use any computing service through your browser without owning anything.
An application of cloud computing is backing your photos to the cloud. Your photos can be backed up to Onedrive or Google. They can easily be accessed on any device, mobile or desktop. The computing service used here is storage, storage for images.
Cloud computing is evolving and has a significant application and advantages for individuals and businesses.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
There are key advantages of cloud computing.
Scalability
Cloud resources can scale up and down to meet workload requirements. This means that companies can provision resources based on their workload. For example, you use Google Photos with 15GB as an individual. You decided to scale up as a business and purchase the 100GB storage. This is scalability based on the business demand.
Cost savings
Cloud computing models use pay-as-you-go pricing which means companies only pay for what they use. This prevents excessive spending on resources not in use.
Innovation
Cloud computing provides easy access to cutting-edge tech like analytics, AI, serverless computing and machine learning. This allows for the innovation of new technologies.
Agility and flexibility
Companies can rapidly provision the resources they need without upfront capital expenses. This allows them to adapt quickly to changes in demand or market conditions.
Reliability
Leading cloud providers deliver a highly reliable infrastructure with built-in redundancy. This makes them reliable, reducing down time in the services they offer.
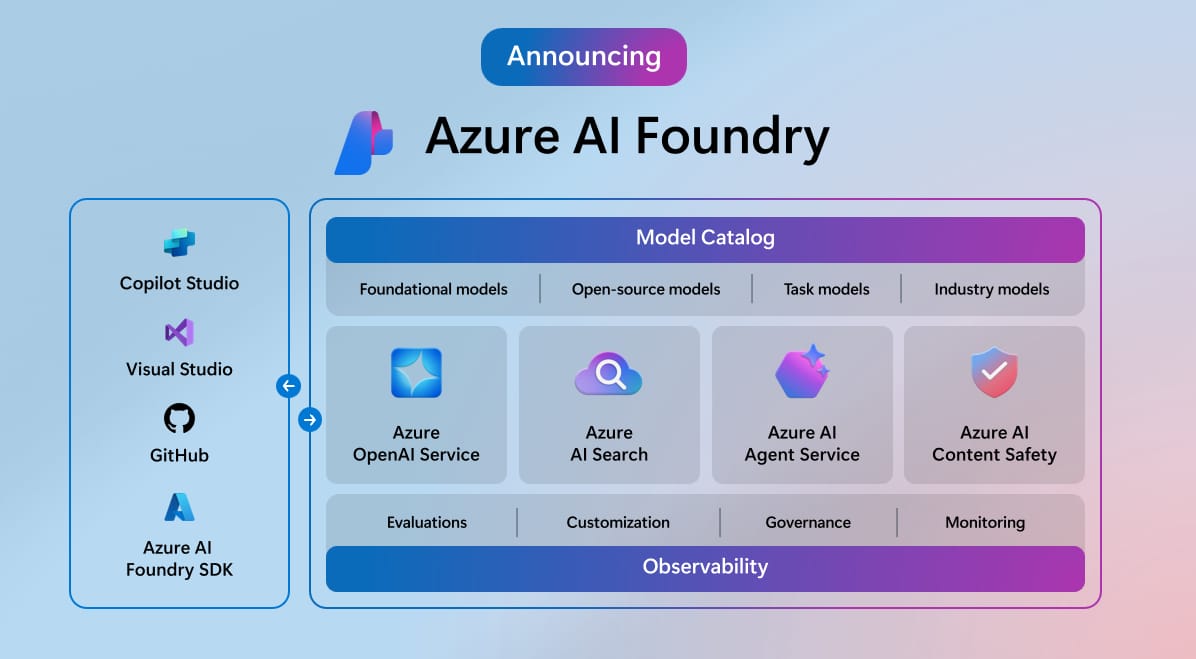
Components of Cloud Computing
There are three main cloud computing models: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).

1. Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) provides basic building blocks for cloud IT like servers, networking, storage, and data centers. It allows companies to outsource infrastructure management to cloud providers. This way, companies do not have physical structures to set up storage, networks, etc. An example of an IaaS application is a Virtual Machine (VM).
Pros:
– No upfront infrastructure costs
– Pay-as-you-go pricing
– Quickly scale resources up or down
– Access to the latest technology
Cons:
– Managing OS, middleware, runtimes, data, and apps still required
– Multi-tenant environments have less control and customization
Use Cases:
– Testing and development environments
– Websites and web apps
– Batch processing
– Big data analysis
2. Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a managed platform for building, running, and managing applications without maintaining infrastructure.
PaaS includes IaaS plus operating systems, middleware, development tools, and more. This allows companies to focus on applications. Examples of Paas applications are- Visual Studio Code and GitHub Online.
Pros:
– Speeds application development
– Support for full app lifecycle
– Multiple languages and frameworks available
– Apps can be quickly built, tested, and deployed
Cons:
– Some platform constraints and customizations are not allowed
– Migrating between platforms can be challenging
Use Cases:
– Web and mobile apps
– APIs
– Business analytics and intelligence
– Integration projects
3. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) provides on-demand access to software applications hosted in the cloud. Companies don’t manage infrastructure or platforms. SaaS gives access to end-user applications over the internet rather than installing locally. Examples of SaaS applications are – Microsoft Word Online, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Excel Online, and Microsoft Outlook.
Pros:
– No upfront costs for hardware or software licenses.
– Automatic updates and patch management.
– Accessible from anywhere with internet connection.
– Usage-based pricing model.
Cons:
– Limited configuration options
– Reliant on vendor’s security measures
– Integration with on-premise systems can be challenging.
Use Cases:
– Email and collaboration tools
– CRM and sales management
– Accounting and finance
– HR and talent management
Get an in-depth knowledge of different Cloud services with our Cloud Computing Courses!
Cloud Deployment Models
There are three main types of cloud deployment models.
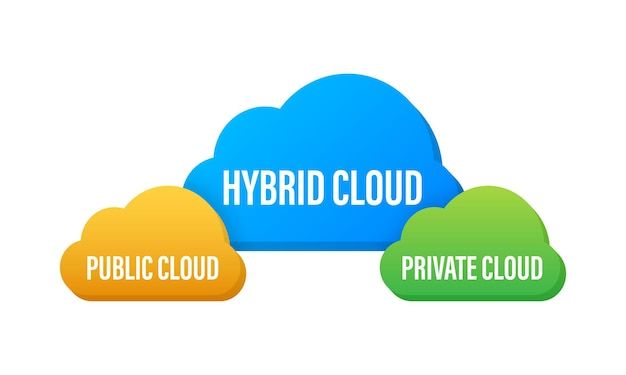
1. Public Cloud
Public cloud services are accessed via a secure network connection (typically over the Internet). They provide resources like servers and storage to multiple organizations and users. They are typically owned and operated by cloud services or hosting Providers.
Examples of Public Cloud Services.
Microsoft Azure, Salesforce, Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM, Oracle, Sap, Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
– Pros: Highly scalable, no upfront infrastructure investment, pay-as-you-go pricing.
– Cons: Less customization and control, potential security and privacy concerns.
– Use Cases: Small businesses, startups, applications.
2. Private Cloud
Private cloud platforms are built exclusively for one organization. They can be hosted on-premises or at a third-party data center. The infrastructure is dedicated to and managed by the organization. They do not provide access to users outside of the organizations and apply restrictions. The organization is responsible for operating the services they provide.
– Pros: Increased security and control, meets compliance requirements, customized to needs
– Cons: Higher upfront costs, maintenance and updates require internal resources
– Use Cases: Enterprises, government agencies, and regulated industries like healthcare
Examples of Private Cloud Services
Dell, VMware, HPE
3. Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid clouds combine public and private clouds, allowing organizations to run some infrastructure internally and some externally. Apps and data can be hosted in the most optimal location. Hybrid cloud combines and unifies public cloud, private cloud and on-premises infrastructure to create a single, flexible, cost-optimal IT infrastructure
– Pros: Flexibility, scalability, and security through both models
– Cons: Complex integration and dependencies across environments
– Use Cases: Organizations operating in regulated industries that still want cloud benefits
Examples of Hybrid Cloud Services.
Rackspace, IBM and CISCO.
Conclusion
The cloud computing field offers many exciting roles with high salaries. As organizations move more business functions to the cloud, there will be continued growth in cloud careers. Developing the right technical skills through certifications and hands-on experience can help land a fulfilling cloud job.
Try our Microsoft 365 Security Training and learn concepts of cloud security!