Careers in Azure | Azure Certifications, Jobs & Salary

Careers in Azure are lucrative, in-demand and have high value. Azure provides a wide range of services for building, deploying, and managing applications. Azure offers over 200 products and cloud services for storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning and more. These services require roles, responsibilities and careers for professionals. This article dives into careers in […]
Microsoft Azure Fundamentals: A Comprehensive Guide

In today’s digital era, cloud computing has become the foundation for many successful businesses. It allows organizations to access resources, storage, and services over the internet. Among the leading cloud service providers, Microsoft Azure stands out due to its robust infrastructure, broad range of services, and commitment to security and compliance. To fully unleash the […]
Major Cloud Service Providers – AWS, Azure, Google Cloud

Cloud service providers play a crucial role in the advancement of cloud computing. They have made cloud services widely available, easily accessible, and beneficial for individuals and businesses. The cloud computing industry boasts numerous service providers, such as Microsoft, Amazon, Google, Oracle, among others. Among the top providers in the market are Microsoft Cloud, Amazon […]
How Migrating to the Cloud Can Transform Your Business

Cloud computing offers numerous benefits for businesses, helping them improve efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. This article expands on how migrating to the cloud transforms businesses, its benefits and practical examples. Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses. Cost Savings One of the benefits of cloud computing for businesses is saving costs. With cloud computing, businesses […]
Mastering IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS for Business Growth
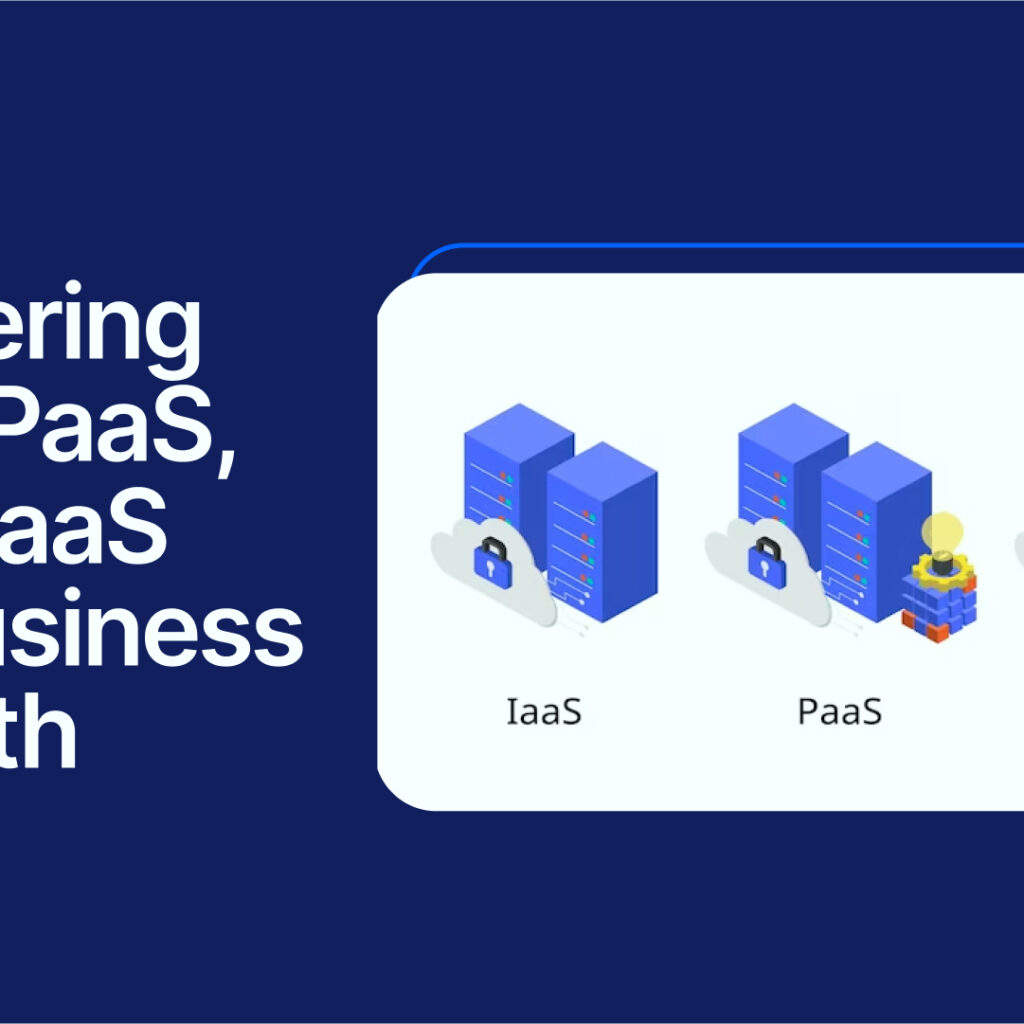
In today’s digital age, cloud computing has transformed the way businesses operate. At the core of cloud computing lie three distinct service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). With its numerous benefits, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, the cloud has become an essential tool […]
Cloud Computing: A Beginner’s Guide.

Cloud computing is one of the most in-demand and lucrative professions in information technology. Organizations are replacing their infrastructure with cloud services and keeping sensitive, critical data in the cloud. Cloud engineering can be used by enterprises in any area, including banking, healthcare, aviation, information technology, and manufacturing. Running businesses using the cloud has encouraged […]
Embarking on a Cloud Journey: Unveiling the Tech Revolution with Evolve Connect
Are you considering a transition into the vast realm of technology? Ever heard of cloud computing? If you’re eager to step into the dynamic world of tech but feel uncertain, especially if coding isn’t your forte, take a moment, grab a refreshing glass of water, and let me introduce you to a captivating realm within […]
Evolve Your Skills: Welcome to Evolve Connect.

Do you want to transition into tech? Have you heard of cloud computing? Are you eager to step into the dynamic world of technology but unsure where to begin, especially if coding is not your area of expertise? Take a moment, grab a refreshing glass of water, and allow me to unveil a captivating realm […]